Firstly, and most importantly, I hope you are in good health and coping well with Covid 19, physically and psychologically. It has been well over a month since I posted my last article. This has been due to some personal change of circumstance, in a good way. Hopefully you all will see more regular posts from me.
with the explosion of IoT sensors and data captured through these devices, user privacy and security remain a major challenge in IoT(specially in healthcare -IoMT). Recently, there has been some research on a possible solution to address this overwhelming security concerns using Blockchain. So, this article is based on my recent talk at an event where I discussed Blockchain of Medical things (BCoMT).
And if you have missed my previous article of Blockchain and healthcare, please visit https://wordpress.com/read/feeds/88857668/posts/2259347247
Blockchain of Medical Things aims to solve the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) security problem using Blockchain. Blockchain and IoT– as standalone technologies – have already proved them to be highly disruptive.
Internet of Medical things (IoMT), which has derived from Internet of Things, is a collection of devices connected to the internet to provide health related services. Basically, IoMT is a connected infrastructure of health system such as medical devices, software applications and services.
On November 2017, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first pill with a sensor inside of it (aripiprazole tablets with sensor) that can track if a patient has swallowed it. This pill’s sensor sends messages to a wearable patch, and the patch itself transmits the message to a mobile application on the smartphone. This technology could be a game changer for chronic disease and mental health disorders.
Blockchain is a peer-to-peer technology for distributed data sharing and computing which provides unalterable and irremovable transactions. By definition, Blockchain (BC) is a type of Distributed Ledger in a temper-proof digital ledger with time stamp.
Since IoMT highly utilises the existing wireless sensor network (wsn) technologies or open internet, intrinsically it remains vulnerable to privacy as well as security threats. The main concern in IoMT is the secure and efficient transmission of the medical data. Healthcare data is a lucrative target for hackers and therefore securing protected health information (PHI) is the primary motivation of healthcare providers. However, the inability to delete or change information from blocks makes blockchain technology a suitable alternative for the healthcare system and could prevent these issues. Blockchain, by its design and architecture- consensus method and cryptographic techniques – is considered as a Trust Machine. Thus, it possesses the potentials to address major share of the security issues found in IoMT.
Scientists argue them to be complementary technologies to each other: BC requires participating nodes for consensus approach which can be supplemented by IoMT devices while IoMT requires security features which can be met by BC such as transparency, privacy, immutability, operational resilience and so forth.
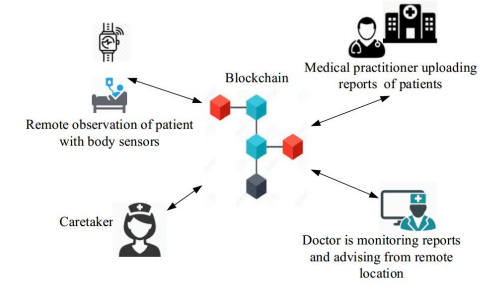
Applying blockchain technology in IoMT cold provide many benefits. Most of the current IoMT ecosystems depend on communication and control models that are centralized. This model has connected generic computing devices and continues to support small-scale IoMT networks. However, the growing need for large-scale, distributed open IoMT systems cannot be satisfied by the centralized communication model and will fully benefit from decentralised approach, which is the core of blockchain based solution.
Key benefits of deploying blockchain are:
- Secure medical records which cannot be completed without the involvement of a trusted intermediary avoiding a performance bottleneck and a single point of failure.
- Patients can access and have control over their data and family members can also view the details of their patient condition.
- Distribution of data is accurate, consistent and timely in blockchain.
- Any change happens in the blockchain can easily be visible by all the members of the patient network.
Final remarks, IoMT privacy and security is one of the most significant challenge in its adoption. On the other hand, Blockchain is evolving as one of the most promising and creative technologies for security. Blockchain holds promise for privacy and security in IoMT. Merging blockchain with the Internet of Medical Things has been provided a decentralized way to manage the rapidly increasing number of IoMT devices.
